An Internet Protocol ( IP ) address is a numerical label that is assigned to devices in a computer network that exchange data according to the Internet Protocol . [ 1 ] An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing . Internet Protocol (IP) address adalah sebuah label numerik yang ditugaskan untuk perangkat dalam jaringan komputer yang bertukar data sesuai dengan Protokol Internet. [1] Sebuah alamat IP memiliki dua fungsi utama: host atau jaringan identifikasi dan lokasi pengalamatan. Its role has been characterized thusly: "A name indicates what we seek. An address indicates where it is. A route indicates how to get there." [ 2 ] Perannya telah ditandai sebagai berikut: untuk "Sebuah nama menunjukkan apa yang kita cari. Sebuah alamat menunjukkan di mana tempatnya. Sebuah rute menunjukkan bagaimana menuju ke sana." [2]
The Internet Protocol also routes data packets between networks, and IP addresses specify the locations of the source and destination nodes in the topology of the routing system. Protokol Internet juga rute data paket di antara jaringan, dan alamat IP menentukan lokasi dari sumber dan tujuan node dalam topologi dari routing sistem. For this purpose, some of the bits in an IP address are used to designate a subnetwork . Untuk tujuan ini, beberapa bit dalam sebuah alamat IP yang digunakan untuk menunjuk Sub-jaringan. The number of these bits is indicated in CIDR notation , appended to the IP address; eg, 208.77.188.166/24 . Jumlah bit ini ditunjukkan dalam notasi CIDR, ditambahkan ke alamat IP, misalnya: 208.77.188.166/24.
With the development of private networks and the threat of IPv4 address exhaustion , a group of private address spaces was set aside by RFC 1918 . Dengan pengembangan jaringan swasta dan ancaman alamat IPv4 kelelahan, sekelompok ruang alamat pribadi disisihkan oleh RFC 1918. These private addresses may be used by anyone on private networks. Alamat swasta ini dapat digunakan oleh siapa saja di jaringan pribadi. They are often used with network address translators to connect to the global public Internet. Mereka sering digunakan dengan penerjemah alamat jaringan untuk menyambung ke Internet publik global.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) manages the IP address space allocations globally. Para IANA (IANA) yang mengelola alokasi ruang alamat IP secara global. IANA works in cooperation with five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) to allocate IP address blocks to Local Internet Registries (Internet service providers) and other entities. IANA bekerja dalam kerjasama dengan lima Regional Internet Registry (RIR) untuk mengalokasikan blok alamat IP untuk Lokal Internet Registries (penyedia layanan Internet) dan entitas lain.
The designers of TCP/IP defined an IP address as a 32-bit number [ 1 ] and this system, known as Internet Protocol Version 4 or IPv4 , is still in use today. Para desainer dari TCP / IP didefinisikan alamat IP sebagai 32-bit [1] dan sistem ini, yang dikenal sebagai Internet Protocol Versi 4 atau IPv4, yang masih digunakan sampai sekarang. The enormous growth of the Internet depleted the pool of available addresses, leading in 1995 to the creation of the 128-bit IPv6 system, [ 3 ] which was last standardized by RFC 2460 in 1998. [ 4 ] Although IP addresses are stored as binary numbers , they are usually displayed in human-readable notations, such as 208.77.188.166 (for IPv4 ), and 2001:db8:0:1234:0:567:1:1 (for IPv6 ). Pertumbuhan yang sangat besar terkuras Internet kolam yang tersedia alamat, terkemuka pada tahun 1995 untuk pembentukan 128-bit IPv6 sistem, [3] yang terakhir distandarisasi oleh RFC 2460 pada tahun 1998. [4] Walaupun alamat IP yang disimpan sebagai biner angka, mereka biasanya ditampilkan dalam terbaca-manusia notasi, seperti 208.77.188.166 (untuk IPv4), dan 2001: db8: 0:1234:0:567:1:1 (untuk IPv6). Because of its prevalence, the generic term IP address typically still refers to the addresses defined by IPv4 . Karena prevalensi, istilah generik alamat IP biasanya masih mengacu ke alamat yang didefinisikan oleh IPv4.
IPv4 vs. IPv6 IPv6 vs IPv4
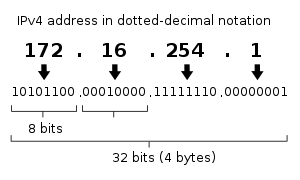
IP version 4 addresses alamat IP versi 4
IPv4 uses 32- bit (4- byte ) addresses, which limits the address space to 4,294,967,296 (2 32 ) possible unique addresses. IPv4 menggunakan 32 - bit (4 - byte) alamat, yang membatasi ruang alamat untuk 4.294.967.296 (2 32) kemungkinan alamat unik. IPv4 reserves some addresses for special purposes such as private networks (~18 million addresses) or multicast addresses (~270 million addresses). Cadangan beberapa alamat IPv4 untuk tujuan khusus seperti jaringan privat (~ 18 juta alamat) atau alamat multicast (~ 270 juta alamat). This reduces the number of addresses that can be allocated to end users and, as the number of addresses available is consumed, IPv4 address exhaustion is inevitable. Hal ini mengurangi jumlah alamat yang dapat dialokasikan kepada pengguna akhir dan, sebagai jumlah alamat yang tersedia adalah dikonsumsi, alamat IPv4 kelelahan tidak dapat dihindari. This foreseeable shortage was the primary motivation for developing IPv6 , which is in various deployment stages around the world and is the only strategy for IPv4 replacement and continued Internet expansion. Kekurangan masa ini adalah motivasi utama untuk mengembangkan IPv6, yang dalam berbagai tahap penyebaran di seluruh dunia dan merupakan satu-satunya strategi untuk IPv4 pengganti dan melanjutkan ekspansi Internet.
IPv4 addresses are usually represented in dot-decimal notation (four numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by dots, eg 208.77.188.166). Biasanya alamat IPv4 direpresentasikan dalam notasi dot-desimal (empat angka, masing-masing berkisar dari 0 hingga 255, dipisahkan oleh titik, misalnya 208.77.188.166). Each part represents 8 bits of the address, and is therefore called an octet . Setiap bagian mewakili 8 bit alamat, dan oleh karena itu disebut sebagai oktet.In less common cases of technical writing, IPv4 addresses may be presented in hexadecimal , octal , or binary representations. Dalam kasus-kasus yang kurang umum penulisan teknis, mungkin alamat IPv4 disajikan dalam heksadesimal, oktal, atau biner representasi. In most representations each octet is converted individually. Pada sebagian besar representasi setiap oktet dikonversi secara individual.
IPv4 subnetting IPv4 subnetting
In the early stages of development of the Internet Protocol, [ 1 ] network administrators interpreted an IP address in two parts, network number portion and host number portion. Pada tahap awal pengembangan Internet Protocol, [1] ditafsirkan administrator jaringan alamat IP dalam dua bagian, jaringan dan host nomor porsi nomor porsi. The highest order octet (most significant eight bits) in an address was designated the network number and the rest of the bits were called the rest field or host identifier and were used for host numbering within a network. Urutan tertinggi oktet (delapan bit paling signifikan) di alamat ditetapkan nomor jaringan dan sisanya bit disebut bidang yang lain, atau host pengenal dan digunakan untuk penomoran host dalam sebuah jaringan. This method soon proved inadequate as additional networks developed that were independent from the existing networks already designated by a network number. Metode ini segera terbukti tidak memadai sebagai tambahan dikembangkan jaringan yang independen dari jaringan yang ada sudah ditunjuk oleh nomor jaringan. In 1981, the Internet addressing specification was revised with the introduction of classful network architecture. [ 2 ] Pada tahun 1981, Internet pengalamatan spesifikasi direvisi dengan pengenalan jaringan classful arsitektur. [2]
Classful network design allowed for a larger number of individual network assignments. Desain jaringan Classful diperbolehkan untuk jumlah yang lebih besar tugas jaringan individu. The first three bits of the most significant octet of an IP address was defined as the class of the address. Tiga bit pertama dari octet paling penting dari sebuah alamat IP didefinisikan sebagai alamat kelas. Three classes ( A , B , and C ) were defined for universal unicast addressing. Tiga kelas (A, B, dan C) yang ditetapkan untuk universal unicast menangani. Depending on the class derived, the network identification was based on octet boundary segments of the entire address. Tergantung pada kelas turunan, identifikasi jaringan didasarkan pada segmen batas oktet seluruh alamat. Each class used successively additional octets in the network identifier, thus reducing the possible number of hosts in the higher order classes ( B and C ). Setiap kelas oktet tambahan berturut-turut digunakan dalam jaringan identifier, sehingga mengurangi jumlah kemungkinan host dalam urutan yang lebih tinggi kelas (B dan C). The following table gives an overview of this now obsolete system. Tabel berikut memberikan gambaran sistem usang sekarang ini.
| Historical classful network architecture Sejarah arsitektur jaringan classful | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class Kelas | First octet in binary Oktet pertama dalam biner | Range of first octet Kisaran oktet pertama | Network ID Network ID | Host ID Host ID | Number of networks Jumlah jaringan | Number of addresses Jumlah alamat |
| A Sebuah | 0XXXXXXX 0XXXXXXX | 0 - 127 0-127 | a sebuah | bcd bcd | 2 7 = 128 2 7 = 128 | 2 24 = 16,777,216 2 24 = 16.777.216 |
| B B | 10XXXXXX 10XXXXXX | 128 - 191 128-191 | ab ab | cd cd | 2 14 = 16,384 2 14 = 16.384 | 2 16 = 65,536 2 16 = 65.536 |
| C C | 110XXXXX 110XXXXX | 192 - 223 192-223 | abc abc | d d | 2 21 = 2,097,152 2 21 = 2.097.152 | 2 8 = 256 2 8 = 256 |
The articles ' subnetwork ' and ' classful network ' explain the details of this design. Artikel 'Sub-jaringan' dan 'jaringan classful' menjelaskan rincian desain ini.
Although classful network design was a successful developmental stage, it proved unscalable in the rapid expansion of the Internet and was abandoned when Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) was created for the allocation of IP address blocks and new rules of routing protocol packets using IPv4 addresses. Meskipun desain jaringan classful adalah tahap perkembangan yang sukses, itu terbukti unscalable dalam ekspansi cepat dari Internet dan ini ditinggalkan saat Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) diciptakan untuk alokasi alamat IP blok dan aturan-aturan baru menggunakan protokol routing paket IPv4 alamat. CIDR is based on variable-length subnet masking (VLSM) to allow allocation and routing on arbitrary-length prefixes. CIDR didasarkan pada variable-length subnet masking (VLSM) untuk memungkinkan alokasi dan routing pada awalan sewenang-wenang-panjang.
Today, remnants of classful network concepts function only in a limited scope as the default configuration parameters of some network software and hardware components (eg netmask), and in the technical jargon used in network administrators' discussions. Saat ini, sisa-sisa dari konsep-konsep jaringan classful fungsi hanya dalam lingkup terbatas sebagai konfigurasi default parameter jaringan beberapa komponen perangkat lunak dan perangkat keras (misalnya netmask), dan dalam bahasa teknis yang digunakan dalam administrator jaringan 'diskusi.
IPv4 private addresses alamat pribadi IPv4
Early network design, when global end-to-end connectivity was envisioned for communications with all Internet hosts, intended that IP addresses be uniquely assigned to a particular computer or device. Desain jaringan awal, ketika akhir global-to-end untuk konektivitas yang dibayangkan komunikasi dengan semua host internet, dimaksudkan bahwa alamat IP secara unik yang diberikan pada sebuah komputer atau perangkat tertentu. However, it was found that this was not always necessary as private networks developed and public address space needed to be conserved ( IPv4 address exhaustion ). Namun, ditemukan bahwa hal ini tidak selalu diperlukan sebagai jaringan swasta dikembangkan dan ruang alamat publik perlu dilestarikan (alamat IPv4 kelelahan).
Computers not connected to the Internet, such as factory machines that communicate only with each other via TCP/IP, need not have globally-unique IP addresses. Komputer tidak terhubung ke Internet, seperti mesin-mesin pabrik yang berkomunikasi hanya dengan satu sama lain melalui TCP / IP, tidak perlu secara global-alamat IP yang unik. Three ranges of IPv4 addresses for private networks , one range for each class ( A , B , C ), were reserved in RFC 1918 . Kisaran tiga alamat IPv4 untuk jaringan swasta, satu rentang untuk setiap kelas (A, B, C), yang dimiliki dalam RFC 1918. These addresses are not routed on the Internet and thus their use need not be coordinated with an IP address registry. Alamat ini tidak diteruskan di Internet dan dengan demikian penggunaannya tidak perlu dikoordinasikan dengan alamat IP registri.
Today, when needed, such private networks typically connect to the Internet through network address translation (NAT). Hari ini, bila diperlukan, seperti jaringan swasta biasanya terhubung ke Internet melalui network address translation (NAT).
| IANA-reserved private IPv4 network ranges IANA-reserved rentang jaringan IPv4 swasta | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Start Mulai | End Akhir | No. of addresses Jumlah alamat | |
| 24-bit Block (/8 prefix, 1 x A) 24-bit Block (/ 8 prefix, 1 x A) | 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 10.255.255.255 | 16,777,216 16.777.216 |
| 20-bit Block (/12 prefix, 16 x B) 20-bit Block (/ 12 prefix, 16 x B) | 172.16.0.0 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 172.31.255.255 | 1,048,576 1.048.576 |
| 16-bit Block (/16 prefix, 256 x C) 16-bit Block (/ 16 prefix, 256 x C) | 192.168.0.0 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 192.168.255.255 | 65,536 65.536 |
Any user may use any of the reserved blocks. Setiap user dapat menggunakan salah satu blok reserved. Typically, a network administrator will divide a block into subnets ; for example, many home routers automatically use a default address range of 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.0.255 (192.168.0.0/24). Biasanya, seorang administrator jaringan akan membagi satu blok ke dalam subnet, misalnya, banyak rumah router secara otomatis menggunakan kisaran alamat default 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.0.255 (192.168.0.0/24).
IPv4 address depletion alamat IPv4 penipisan
The IP version 4 address space is rapidly nearing exhaustion of available, officially assignable address blocks. IP versi 4 ruang alamat ini dengan cepat hampir kelelahan yang tersedia, secara resmi alamat dialihkan blok.
IP version 6 addresses alamat IP versi 6
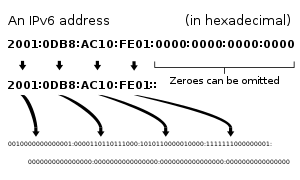
The rapid exhaustion of IPv4 address space, despite conservation techniques, prompted the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to explore new technologies to expand the Internet's addressing capability. Kelelahan yang cepat ruang alamat IPv4, meskipun teknik konservasi, mendorong Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) untuk mengeksplorasi teknologi baru untuk memperluas kemampuan pengalamatan Internet. The permanent solution was deemed to be a redesign of the Internet Protocol itself. Solusi permanen itu dianggap sebagai mendesain ulang Internet Protokol itu sendiri. This next generation of the Internet Protocol, aimed to replace IPv4 on the Internet, was eventually named Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) in 1995 [ 3 ] [ 4 ] The address size was increased from 32 to 128 bits or 16 octets , which, even with a generous assignment of network blocks, is deemed sufficient for the foreseeable future. Ini generasi berikutnya dari Internet Protocol, yang ditujukan untuk menggantikan IPv4 di Internet, akhirnya bernama Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) pada tahun 1995 [3] [4] Alamat meningkat ukuran 32-128 bit atau 16 oktet, yang, bahkan dengan tugas murah blok jaringan, dianggap cukup untuk masa yang akan datang. Mathematically, the new address space provides the potential for a maximum of 2 128 , or about 3.403 × 10 38 unique addresses. Matematis, ruang alamat baru menyediakan potensi untuk maksimum 2 128, atau kira-kira 3,403 × 10 38 alamat unik.
The new design is not based on the goal to provide a sufficient quantity of addresses alone, but rather to allow efficient aggregation of subnet routing prefixes to occur at routing nodes. Desain baru ini tidak didasarkan pada tujuan untuk memberikan jumlah yang cukup alamat sendirian, melainkan untuk memungkinkan agregasi efisien prefiks subnet routing routing terjadi pada node. As a result, routing table sizes are smaller, and the smallest possible individual allocation is a subnet for 2 64 hosts, which is the square of the size of the entire IPv4 Internet. Akibatnya, ukuran tabel routing lebih kecil, dan alokasi individu terkecil yang mungkin adalah sebuah subnet untuk 2 64 host, yang merupakan kuadrat dari ukuran seluruh internet IPv4. At these levels, actual address utilization rates will be small on any IPv6 network segment. Pada tingkat ini, tingkat pemanfaatan alamat sebenarnya akan menjadi kecil pada setiap segmen jaringan IPv6. The new design also provides the opportunity to separate the addressing infrastructure of a network segment—that is the local administration of the segment's available space—from the addressing prefix used to route external traffic for a network. Desain baru ini juga memberikan kesempatan untuk memisahkan pengalamatan jaringan infrastruktur yang segmen-administrasi lokal segmen yang tersedia ruang-dari awalan pengalamatan eksternal digunakan untuk rute lalu lintas jaringan. IPv6 has facilities that automatically change the routing prefix of entire networks should the global connectivity or the routing policy change without requiring internal redesign or renumbering. IPv6 memiliki fasilitas yang secara otomatis mengubah awalan routing seluruh jaringan harus konektivitas global atau perubahan kebijakan routing tanpa memerlukan redesign atau renumbering internal.
The large number of IPv6 addresses allows large blocks to be assigned for specific purposes and, where appropriate, to be aggregated for efficient routing. Banyaknya alamat IPv6 memungkinkan besar blok yang akan ditetapkan untuk tujuan tertentu, dan, bila sesuai, yang akan digabungkan untuk efisiensi routing. With a large address space, there is not the need to have complex address conservation methods as used in classless inter-domain routing (CIDR). Dengan ruang alamat yang besar, tidak ada kebutuhan untuk memiliki metode konservasi alamat yang kompleks seperti yang digunakan dalam tanpa kelas antar-domain routing (CIDR).
All modern [update] desktop and enterprise server operating systems include native support for the IPv6 protocol, but it is not yet widely deployed in other devices, such as home networking routers, voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and multimedia equipment, and network peripherals. Semua modern [update] desktop dan server perusahaan sistem operasi meliputi dukungan asli untuk protokol IPv6, tapi belum secara luas digunakan di perangkat lain, seperti router jaringan rumah, suara over Internet Protocol (VoIP) dan peralatan multimedia, dan perangkat jaringan .
Example of an IPv6 address: Contoh alamat IPv6:
2001:0db8:85a3:08d3:1319:8a2e:0370:7334 2001:0 db8: 85a3: 08d3: 1319:8 a2e: 0370:7334
IPv6 private addresses IPv6 alamat pribadi
Just as IPv4 reserves addresses for private or internal networks, there are blocks of addresses set aside in IPv6 for private addresses. Sama seperti alamat IPv4 cadangan untuk pribadi atau jaringan internal, ada blok alamat IPv6 menyisihkan di alamat pribadi. In IPv6, these are referred to as unique local addresses (ULA). RFC 4193 sets aside the routing prefix fc00::/7 for this block which is divided into two /8 blocks with different implied policies (cf. IPv6 ) The addresses include a 40-bit pseudorandom number that minimizes the risk of address collisions if sites merge or packets are misrouted. Dalam IPv6, ini disebut sebagai alamat lokal yang unik (ULA). RFC 4.193 set routing prefiks ke samping fc00:: / 7 untuk blok ini yang terbagi menjadi dua / 8 blok dengan kebijakan tersirat yang berbeda (bdk. IPv6) Alamat meliputi 40-bit pseudorandom nomor yang meminimalkan risiko alamat situs tabrakan jika merger atau paket misrouted.
Early designs ( RFC 3513 ) used a different block for this purpose (fec0::), dubbed site-local addresses. Desain awal (RFC 3513) menggunakan blok yang berbeda untuk tujuan ini (fec0::), dijuluki alamat situs-lokal. However, the definition of what constituted sites remained unclear and the poorly defined addressing policy created ambiguities for routing. Namun, definisi situs apa yang membentuk masih belum jelas dan kurang didefinisikan kebijakan mengatasi ambiguitas diciptakan untuk routing. The address range specification was abandoned and must no longer be used in new systems. Rentang alamat spesifikasi ditinggalkan dan harus tidak lagi digunakan dalam sistem baru.
Addresses starting with fe80: — called link-local addresses — are assigned only in the local link area. Alamat dimulai dengan fe80: - disebut link-alamat lokal - hanya ditugaskan di wilayah link lokal. The addresses are generated usually automatically by the operating system's IP layer for each network interface. Alamat biasanya dihasilkan secara otomatis oleh sistem operasi IP untuk masing-masing lapisan antarmuka jaringan. This provides instant automatic network connectivity for any IPv6 host and means that if several hosts connect to a common hub or switch, they have an instant communication path via their link-local IPv6 address. Hal ini menyediakan konektivitas jaringan otomatis instan untuk setiap IPv6 host dan berarti jika beberapa host yang terhubung ke sebuah hub atau switch umum, mereka memiliki jalur komunikasi instan melalui link-lokal mereka alamat IPv6. This feature is used extensively, and invisibly to most users, in the lower layers of IPv6 network administration (cf. Neighbor Discovery Protocol ). Fitur ini digunakan secara luas, dan tak terlihat bagi kebanyakan pengguna, di lapisan bawah administrasi jaringan IPv6 (bdk. Neighbor Discovery Protocol).
None of the private address prefixes may be routed in the public Internet. Tak satu pun dari prefiks alamat swasta mungkin akan diarahkan dalam Internet publik.
IP subnetworks IP subnetwork
The technique of subnetting can operate in both IPv4 and IPv6 networks. Teknik subnetting dapat beroperasi di kedua jaringan IPv4 dan IPv6. The IP address is divided into two parts: the network address and the host identifier . Alamat IP dibagi menjadi dua bagian: alamat jaringan dan host identifier. The subnet mask (in IPv4 only) or the CIDR prefix determines how the IP address is divided into network and host parts. The subnet mask (di IPv4 hanya) atau CIDR awalan menentukan bagaimana alamat IP dibagi ke dalam jaringan dan bagian host.
The term subnet mask is only used within IPv4. Istilah subnet mask hanya digunakan dalam IPv4. Both IP versions however use the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) concept and notation. Namun kedua versi IP menggunakan Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) konsep dan notasi. In this, the IP address is followed by a slash and the number (in decimal) of bits used for the network part, also called the routing prefix . Dalam hal ini, alamat IP ini diikuti oleh tanda garis miring dan angka (dalam desimal) bit yang digunakan untuk bagian jaringan, juga disebut prefix routing. For example, an IPv4 address and its subnet mask may be 192.0.2.1 and 255.255.255.0, respectively. Sebagai contoh, sebuah alamat IPv4 dan mungkin subnet mask 192.0.2.1 dan 255.255.255.0, masing-masing. The CIDR notation for the same IP address and subnet is 192.0.2.1/24, because the first 24 bits of the IP address indicate the network and subnet. Para notasi CIDR yang sama untuk alamat IP dan subnet 192.0.2.1/24, karena 24 bit pertama dari alamat IP jaringan dan menunjukkan subnet.
Static and dynamic IP addresses statis dan alamat IP dinamis
When a computer is configured to use the same IP address each time it powers up, this is known as a Static IP address . Ketika komputer dikonfigurasi untuk menggunakan alamat IP yang sama setiap kali kekuatan atas, ini dikenal sebagai alamat IP statis. In contrast, in situations when the computer's IP address is assigned automatically, it is known as a Dynamic IP address. Sebaliknya, dalam situasi ketika alamat IP komputer diberikan secara otomatis, itu dikenal sebagai alamat IP dinamis.
Method of assignment Metode penugasan
Static IP addresses are manually assigned to a computer by an administrator. Alamat IP statis ditugaskan secara manual ke komputer oleh administrator. The exact procedure varies according to platform. Prosedur yang bervariasi sesuai dengan platform. This contrasts with dynamic IP addresses, which are assigned either by the computer interface or host software itself, as in Zeroconf , or assigned by a server using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Hal ini berbeda dengan alamat IP dinamis, yang diberikan baik oleh antarmuka atau host komputer software itu sendiri, seperti dalam Zeroconf, atau diserahkan oleh server menggunakan Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Even though IP addresses assigned using DHCP may stay the same for long periods of time, they can generally change. Walaupun alamat IP yang ditetapkan menggunakan DHCP dapat tetap sama untuk jangka waktu yang lama, mereka umumnya dapat berubah. In some cases, a network administrator may implement dynamically assigned static IP addresses. Dalam beberapa kasus, seorang administrator jaringan yang ditetapkan secara dinamis dapat mengimplementasikan alamat IP statis. In this case, a DHCP server is used, but it is specifically configured to always assign the same IP address to a particular computer. Dalam kasus ini, sebuah server DHCP digunakan, tetapi secara khusus dikonfigurasi untuk selalu memberikan alamat IP yang sama untuk komputer tertentu. This allows static IP addresses to be configured centrally, without having to specifically configure each computer on the network in a manual procedure. Hal ini memungkinkan alamat IP statis dapat dikonfigurasi secara terpusat, tanpa harus mengkonfigurasi secara khusus setiap komputer di jaringan dalam prosedur manual.
In the absence or failure of static or stateful (DHCP) address configurations, an operating system may assign an IP address to a network interface using state-less autoconfiguration methods, such as Zeroconf . Dalam ketiadaan atau kegagalan statis atau stateful (DHCP) alamat konfigurasi, sistem operasi dapat menetapkan alamat IP untuk sebuah antarmuka jaringan yang menggunakan kurang autoconfiguration negara-metode, seperti Zeroconf.
Uses of dynamic addressing Penggunaan alamat dinamis
Dynamic IP addresses are most frequently assigned on LANs and broadband networks by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers. Alamat IP dinamis adalah yang paling sering ditugaskan di LAN dan jaringan broadband oleh Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. They are used because it avoids the administrative burden of assigning specific static addresses to each device on a network. Mereka digunakan karena menghindari beban administrasi menentukan alamat statis spesifik untuk setiap perangkat pada jaringan. It also allows many devices to share limited address space on a network if only some of them will be online at a particular time. Hal ini juga memungkinkan banyak perangkat untuk berbagi ruang alamat yang terbatas di dalam sebuah jaringan jika hanya beberapa dari mereka akan online di waktu tertentu. In most current desktop operating systems, dynamic IP configuration is enabled by default so that a user does not need to manually enter any settings to connect to a network with a DHCP server. Dalam sebagian besar sistem operasi desktop saat ini, konfigurasi IP dinamis diaktifkan secara default, sehingga pengguna tidak perlu memasukkan pengaturan secara manual untuk terhubung ke jaringan dengan DHCP server. DHCP is not the only technology used to assigning dynamic IP addresses. DHCP bukan satu-satunya teknologi yang digunakan untuk menentukan alamat IP dinamis. Dialup and some broadband networks use dynamic address features of the Point-to-Point Protocol . Dialup dan beberapa jaringan broadband menggunakan fitur alamat dinamis dari Point-to-Point Protocol.
Sticky dynamic IP address Sticky alamat IP dinamis
A sticky dynamic IP address or sticky IP is an informal term used by cable and DSL Internet access subscribers to describe a dynamically assigned IP address that does not change often. Sebuah alamat IP dinamis lengket atau lengket informal IP adalah istilah yang digunakan oleh kabel dan DSL pelanggan akses Internet untuk menggambarkan sebuah alamat IP yang ditetapkan secara dinamis yang sering tidak berubah. The addresses are usually assigned with the DHCP protocol. Alamat ini biasanya diberikan dengan protokol DHCP. Since the modems are usually powered-on for extended periods of time, the address leases are usually set to long periods and simply renewed upon expiration. Karena biasanya modem powered-on untuk waktu yang lama, alamat sewa biasanya ditetapkan untuk jangka waktu yang lama dan hanya diperbaharui pada kadaluwarsa. If a modem is turned off and powered up again before the next expiration of the address lease, it will most likely receive the same IP address. Jika modem dimatikan dan menyala lagi sebelum berakhirnya masa berikutnya alamat sewa, maka kemungkinan besar akan menerima alamat IP yang sama.
Address autoconfiguration Alamat autoconfiguration
RFC 3330 defines an address block, 169.254.0.0/16, for the special use in link-local addressing for IPv4 networks. 3.330 RFC mendefinisikan alamat blok, 169.254.0.0/16, untuk digunakan khusus dalam link-lokal untuk IPv4 pengalamatan jaringan. In IPv6 , every interface, whether using static or dynamic address assignments, also receives a local-link address automatically in the fe80::/10 subnet. Dalam IPv6, setiap antarmuka, apakah menggunakan alamat statis atau dinamis tugas, juga menerima alamat link lokal secara otomatis dalam fe80:: / 10 subnet.
These addresses are only valid on the link, such as a local network segment or point-to-point connection, that a host is connected to. Alamat ini hanya berlaku pada link, seperti segmen jaringan lokal atau point-to-point koneksi, bahwa sebuah host yang terhubung ke. These addresses are not routable and like private addresses cannot be the source or destination of packets traversing the Internet. Alamat ini tidak routable dan seperti alamat pribadi tidak dapat menjadi sumber atau tujuan dari paket melintasi Internet.
When the link-local IPv4 address block was reserved, no standards existed for mechanisms of address autoconfiguration. Ketika link-blok alamat IPv4 lokal itu dilindungi undang-undang, tidak ada standar mekanisme ada untuk alamat autoconfiguration. Filling the void, Microsoft created an implementation that called Automatic Private IP Addressing ( APIPA ). Mengisi kekosongan, Microsoft menciptakan sebuah implementasi yang disebut Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA). Due to Microsoft's market power, APIPA has been deployed on millions of machines and has, thus, become a de facto standard in the industry. Karena kekuatan pasar Microsoft, APIPA telah digunakan pada jutaan mesin dan memiliki, dengan demikian, menjadi suatu de facto standar dalam industri. Many years later, the IETF defined a formal standard for this functionality, RFC 3927 , entitled Dynamic Configuration of IPv4 Link-Local Addresses . Bertahun-tahun kemudian, IETF didefinisikan standar formal untuk fungsi ini, RFC 3927, yang berjudul Konfigurasi Dinamis IPv4 Link-Local Addresses.
Uses of static addressing Penggunaan alamat statis
Some infrastructure situations have to use static addressing, such as when finding the Domain Name System host that will translate domain names to IP addresses. Beberapa situasi infrastruktur harus menggunakan alamat statis, seperti ketika menemukan Domain Name System host yang akan menerjemahkan nama domain ke alamat IP. Static addresses are also convenient, but not absolutely necessary, to locate servers inside an enterprise. Alamat-alamat statis juga nyaman, tetapi tidak mutlak perlu, untuk menempatkan server di dalam suatu perusahaan. An address obtained from a DNS server comes with a time to live , or caching time , after which it should be looked up to confirm that it has not changed. Alamat yang diperoleh dari server DNS datang dengan waktu untuk hidup, atau caching waktu, setelah itu harus mendongak untuk memastikan bahwa hal itu tidak berubah. Even static IP addresses do change as a result of network administration ( RFC 2072 ) Bahkan alamat IP statis melakukan perubahan sebagai akibat dari administrasi jaringan (RFC 2072)
Modifications to IP addressing Modifikasi ke IP pengalamatan
IP blocking and firewalls IP blocking dan firewall
Firewalls are common on today [update] 's Internet. Firewall adalah umum pada hari ini [update] 's Internet. For increased network security, they control access to private networks based on the public IP of the client. Untuk meningkatkan keamanan jaringan, mereka mengontrol akses ke jaringan pribadi yang didasarkan pada IP publik klien. Whether using a blacklist or a whitelist , the IP address that is blocked is the perceived public IP address of the client, meaning that if the client is using a proxy server or NAT , blocking one IP address might block many individual people. Apakah menggunakan daftar hitam atau daftar putih, alamat IP yang diblokir adalah alamat IP publik yang dirasakan klien, yang berarti bahwa jika klien menggunakan server proxy atau NAT, menghalangi satu alamat IP mungkin blok banyak orang individu.
IP address translation IP address translation
Multiple client devices can appear to share IP addresses: either because they are part of a shared hosting web server environment or because an IPv4 network address translator (NAT) or proxy server acts as an intermediary agent on behalf of its customers, in which case the real originating IP addresses might be hidden from the server receiving a request . Klien beberapa perangkat dapat muncul untuk berbagi alamat IP: entah karena mereka adalah bagian dari sebuah shared hosting server web lingkungan atau karena sebuah alamat IPv4 network address translator (NAT) atau server proxy bertindak sebagai perantara agen atas nama para pelanggan, dalam hal ini alamat IP yang berasal nyata mungkin tersembunyi dari server menerima permintaan. A common practice is to have a NAT hide a large number of IP addresses in a private network . Praktik yang umum adalah memiliki NAT menyembunyikan sejumlah besar alamat IP dalam sebuah jaringan pribadi. Only the "outside" interface(s) of the NAT need to have Internet-routable addresses [ 5 ] . Hanya "di luar" interface (s) dari NAT harus memiliki alamat internet-routable [5].
Most commonly, the NAT device maps TCP or UDP port numbers on the outside to individual private addresses on the inside. Paling umum, perangkat NAT peta TCP atau UDP nomor port di luar untuk masing-masing alamat pribadi di dalam. Just as a telephone number may have site-specific extensions, the port numbers are site-specific extensions to an IP address. Sama seperti nomor telepon mungkin memiliki ekstensi spesifik lokasi, nomor port selalu situs-ekstensi spesifik ke alamat IP.
In small home networks, NAT functions usually take place in a residential gateway device, typically one marketed as a "router". Jaringan rumah kecil, fungsi NAT biasanya berlangsung di sebuah gerbang perumahan perangkat, biasanya satu dipasarkan sebagai "router". In this scenario, the computers connected to the router would have 'private' IP addresses and the router would have a 'public' address to communicate with the Internet. Dalam skenario ini, komputer yang terhubung ke router akan memiliki 'privat' alamat IP dan router akan memiliki 'publik' address untuk berkomunikasi dengan Internet. This type of router allows several computers to share one public IP address. Jenis router ini memungkinkan beberapa komputer untuk berbagi satu alamat IP publik.








